In 30 Seconds: New Battery Breaks Patterns
The most common problem of modern powerful smartphones is the high energy consumption, and therefore the rapid discharge of the battery.
On the one hand, this limits the power growth of portable devices; on the other hand, it forces engineers to upgrade and strengthen compact power supplies. And while some increase energy consumption and optimize consumption, South Korean scientists decided to go on the other side and developed an ultra-fast charging battery.
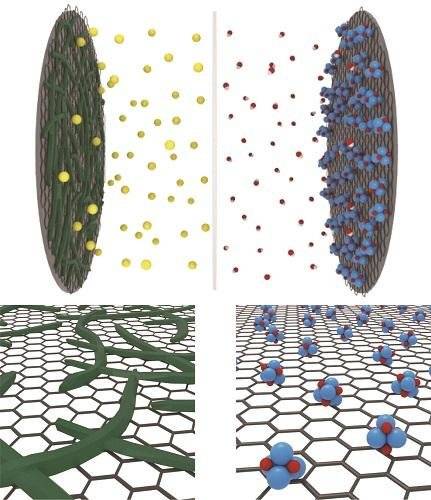
Researchers at the Higher School of Energy under the leadership of Professor Ching Ku Kang have combined fiber-like polymer chains and metal oxide nanocathodes on the surface of graphene, taken as the basis of the product. The choice of graphene as a base is justified by the fact that the structure of this material provides an increased storage area, and therefore increases the battery capacity. The resulting battery can be charged even using a low-power USB-connector in just 20-30 seconds.
In addition to ultra-fast charging, the advantages of this invention include the long service life, high environmental friendliness of conventional batteries, and the ease of production, which allows us to hope for the arrival of this miracle soonequipment into mass production.
On the one hand, this limits the power growth of portable devices; on the other hand, it forces engineers to upgrade and strengthen compact power supplies. And while some increase energy consumption and optimize consumption, South Korean scientists decided to go on the other side and developed an ultra-fast charging battery.
Researchers at the Higher School of Energy under the leadership of Professor Ching Ku Kang have combined fiber-like polymer chains and metal oxide nanocathodes on the surface of graphene, taken as the basis of the product. The choice of graphene as a base is justified by the fact that the structure of this material provides an increased storage area, and therefore increases the battery capacity. The resulting battery can be charged even using a low-power USB-connector in just 20-30 seconds.

In addition to ultra-fast charging, the advantages of this invention include the long service life, high environmental friendliness of conventional batteries, and the ease of production, which allows us to hope for the arrival of this miracle soonequipment into mass production.

Information